An Architectural Guide to Roman/Byzantine Beth-Shean
Sidebar to: Glorious Beth-Shean
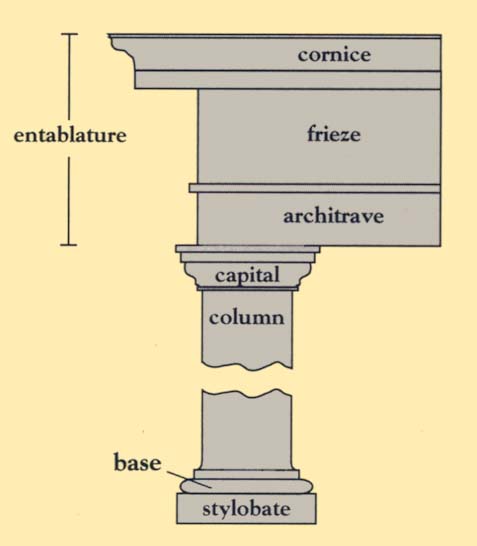
architrave (AR-key-trayve): the continuous, beam-like horizontal architectural feature—often decorated or inscribed—that rests on column capitals.
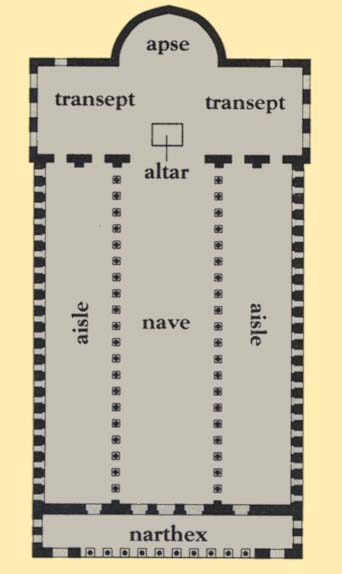
basilica (beh-SILL-eh-kuh): a large, multi-purpose public hall, typically consisting of a nave (see below), side aisles and a semicircular apse. An important influence on church, as well as synagogue, architecture of the fourth century and after.
cornice (CORE-nees): a prominent, continuous horizontal projecting feature surmounting a wall or other construction.
hypocaust (HlGH-peh-cost): a central heating system in which short column stubs support a floor and allow heat from an adjoining furnace room to circulate and heat the room above.
naos (NAY-os): the principal chamber of a classical temple; the shrine.
nave: the central aisle of a church, synagogue or temple, extending from the main entrance to the altar area; columns often flank the sides of a nave, separating it from parallel aisles of less height and width.
nymphaeum (nim-FAY-uhm): an elaborate fountain, sometimes decorated with statuary.
odeon (oh-DEE-on), also odeum: a small theater for musical or other performances; usually roofed.
Already a library member? Log in here.
Institution user? Log in with your IP address.